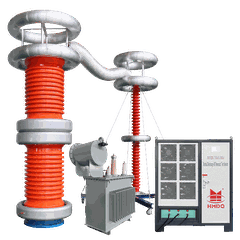
Designing a cascade test transformer is a complex yet rewarding endeavor, especially when you're a supplier in the industry. As a professional in this field, I've witnessed firsthand the importance of a well - designed cascade test transformer in various high - voltage testing applications. In this blog, I'll share some key aspects of designing a cascade test transformer based on my experience.
Understanding the Basics of Cascade Test Transformers
Before delving into the design process, it's crucial to understand what a cascade test transformer is. A cascade test transformer is a specialized type of transformer used for high - voltage testing. It consists of multiple single - phase transformers connected in cascade to achieve high output voltages. The primary advantage of the cascade arrangement is that it allows for the generation of extremely high voltages using transformers with relatively low individual ratings.
The basic principle behind a cascade test transformer is the step - up of voltage through multiple stages. Each stage adds to the overall output voltage, and the insulation of the transformer windings must be carefully designed to withstand the high voltages.
Design Considerations
1. Voltage and Power Requirements
The first step in designing a cascade test transformer is to determine the required output voltage and power. This depends on the specific application for which the transformer will be used. For example, in power system testing, high - voltage testing may be required to simulate over - voltage conditions. The output voltage should be sufficient to perform these tests accurately.
When calculating the power requirements, factors such as the load impedance and the duration of the test must be considered. A higher power rating is necessary for longer test durations or when testing loads with lower impedance.
2. Insulation Design
Insulation is one of the most critical aspects of cascade test transformer design. The insulation system must be able to withstand the high voltages generated during operation without breaking down. Different types of insulation materials can be used, such as oil - impregnated paper, epoxy resin, and SF6 gas.
The design of the insulation structure should take into account factors like the electric field distribution, the temperature rise during operation, and the mechanical stresses on the insulation. For example, the winding insulation should be designed to prevent partial discharges, which can lead to insulation degradation over time.
3. Cooling System
Cascade test transformers generate heat during operation, especially when operating at high power levels. A proper cooling system is essential to maintain the temperature of the transformer within acceptable limits. There are several types of cooling systems available, including air - cooling, oil - cooling, and water - cooling.
Air - cooling is suitable for smaller transformers with lower power ratings. Oil - cooling is a common choice for medium - to - large - sized transformers, as oil has good heat - transfer properties and can also act as an insulation medium. Water - cooling is often used for high - power transformers, as it provides more efficient cooling. You can find more information about related testing equipment like the Water - cooled Generator Insulation Resistance Tester.


4. Winding Design
The winding design of a cascade test transformer is crucial for achieving the desired voltage ratio and performance. The primary and secondary windings should be designed to minimize leakage inductance and resistance. The number of turns in each winding depends on the voltage ratio and the power requirements.
The winding arrangement also affects the electromagnetic compatibility of the transformer. Proper shielding and grounding techniques should be used to reduce electromagnetic interference.
Step - by - Step Design Process
1. Specification Definition
Based on the customer's requirements, define the technical specifications of the cascade test transformer, including the output voltage, power rating, frequency, and insulation level. This step involves close communication with the customer to ensure that all their needs are met.
2. Conceptual Design
Develop a conceptual design of the transformer, including the overall structure, the number of stages in the cascade, and the type of insulation and cooling systems. This design should be optimized for cost, performance, and reliability.
3. Detailed Design
Once the conceptual design is approved, proceed with the detailed design. This includes the design of the windings, the core, the insulation system, and the cooling system. Use advanced engineering software to simulate the performance of the transformer under different operating conditions.
4. Manufacturing and Testing
After the detailed design is completed, start the manufacturing process. Use high - quality materials and advanced manufacturing techniques to ensure the quality of the transformer. Once the manufacturing is finished, conduct a series of tests, including Power Frequency withstand Voltage Control Box tests, to verify the performance of the transformer.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance is an integral part of the design and manufacturing process. Implement a comprehensive quality management system to ensure that all components of the cascade test transformer meet the required standards. This includes inspecting the raw materials, monitoring the manufacturing process, and conducting thorough testing before the transformer is shipped to the customer.
Application in the Industry
Cascade test transformers are widely used in various industries, such as power generation, transmission, and distribution. In the power generation industry, they are used to test the insulation of generators, such as in the case of the Generator Power Frequency Tester. In the transmission and distribution sectors, they are used to test the insulation of high - voltage cables, switchgear, and transformers.
Conclusion
Designing a cascade test transformer requires a deep understanding of electrical engineering principles, insulation technology, and manufacturing processes. By carefully considering the voltage and power requirements, insulation design, cooling system, and winding design, a high - performance cascade test transformer can be developed.
As a cascade test transformer supplier, we are committed to providing high - quality products that meet the diverse needs of our customers. If you are in the market for a cascade test transformer or have any questions about our products, please feel free to contact us for procurement and further discussions.
References
- Grover, F. W. (1946). Inductance Calculations: Working Formulas and Tables. Dover Publications.
- Westinghouse Electric Corporation. (1964). Electrical Transmission and Distribution Reference Book. Westinghouse Electric Corporation.
- IEEE Std C57.12.00 - 2010, IEEE Standard General Requirements for Liquid - Immersed Distribution, Power, and Regulating Transformers.